Pheriperal devices
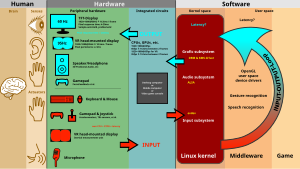
Human Machine Interface (HMI) peripherals.
A peripheral is "an ancillary device used to put information into and get information out of the computer".[1]
There are three different types of peripherals:
- input devices, which interact with or send data from the user to the computer (mice, keyboards, etc.)
- output devices, which provide output to the user from the computer (monitors, printers, etc.)
- input/output devices that perform both functions.
Touchscreens are an example that combines different devices into a single hardware component that can be used both as an input and output device.
A peripheral device is generally defined as any auxiliary device such as a computer mouse orkeyboard that connects to and works with the computer in some way. Other examples of peripherals are image scanners, tape drives,microphones, loudspeakers, webcams, anddigital cameras. Many modern devices, such as digital watches, smartphones and tablet computers, have interfaces that allow them to be used as a peripheral by desktop computers, although they are not host-dependent in the same way as other peripheral devices.
Common input peripherals include keyboards,computer mice, graphic tablets, touchscreens,barcode readers, image scanners,microphones, webcams, game controllers,light pens, and digital cameras. Common output peripherals include computer displays,printers, projectors, and computer speakers.

PDP-11 CPU board
Computer hardware is the physical parts or components of a computer, such as themonitor, keyboard, computer data storage,graphic card, sound card and motherboard.[1]By contrast, software is instructions that can be stored and ran by hardware.
Hardware is directed by the software to execute any command or instruction. A combination of hardware and software forms a usable computing system.
Von Neumann architecture
The template for all modern computers is theVon Neumann architecture, detailed in a 1945 paper by Hungarian mathematician John von Neumann. This describes a design architecture for an electronic digital computerwith subdivisions of a processing unitconsisting of an arithmetic logic unit andprocessor registers, a control unit containing an instruction register and program counter, amemory to store both data and instructions, external mass storage, and input and outputmechanisms.[2] The meaning of the term has evolved to mean a stored-program computerin which an instruction fetch and a data operation cannot occur at the same time because they share a common bus. This is referred to as the Von Neumann bottleneckand often limits the performance of the system.[3]
Sales
Different systems
There are a number of different types of computer system in use today.
Personal computer

Basic hardware components of a modern personal computer, including a monitor, a motherboard, a CPU, aRAM, two expansion cards, a power supply, an optical disc drive, a hard disk drive, a keyboard and a mouse
The personal computer, also known as the PC, is one of the most common types of computer due to its versatility and relatively low price. Laptops are generally very similar, although they may use lower-power or reduced size components, thus lower performance.
Case
The computer case encloses most of the components of the system. It provides mechanical support and protection for internal elements such as the motherboard, disk drives, and power supplies, and controls and directs the flow of cooling air over internal components. The case is also part of the system to control electromagnetic interference radiated by the computer, and protects internal parts from electrostatic discharge. Large tower cases provide extra internal space for multiple disk drives or other peripherals and usually stand on the floor, while desktop cases provide less expansion room. All-in-one style designs from Apple, namely the iMac, and similar types, include a video display in the same case. Portable and laptop computers require cases that provide impact protection for the unit. A current development in laptop computers is a detachable keyboard, which allows the system to be configured as a touch-screen tablet. Hobbyists may decorate the cases with colored lights, paint, or other features, in an activity called case modding.
Power supply
A power supply unit (PSU) converts alternating current (AC) electric power to low-voltage DC power for the internal components of the computer. Laptops are capable of running from a built-in battery, normally for a period of hours.[5]
Motherboard
The motherboard is the main component of a computer. It is a board with integrated circuitry that connects the other parts of the computer including the CPU, the RAM, the disk drives (CD, DVD, hard disk, or any others) as well as any peripherals connected via the ports or the expansion slots.
Components directly attached to or to part of the motherboard include:
- The CPU (Central Processing Unit), which performs most of the calculations which enable a computer to function, and is sometimes referred to as the brain of the computer. It is usually cooled by a heatsink and fan, or water-cooling system. Most newer CPUs include an on-die Graphics Processing Unit (GPU). The clock speed of CPUs governs how fast it executes instructions, and is measured in GHz; typical values lie between 1 GHz and 5 GHz. Many modern computers have the option to overclock the CPU which enhances performance at the expense of greater thermal output and thus a need for improved cooling.
- The chipset, which includes the north bridge, mediates communication between the CPU and the other components of the system, including main memory.
- Random-Access Memory (RAM), which stores the code and data that are being actively accessed by the CPU. For example, when a web browser is opened on the computer it takes up memory; this is stored in the RAM until the web browser is closed. RAM usually comes on DIMMs in the sizes 2GB, 4GB, and 8GB, but can be much larger.
- Read-Only Memory (ROM), which stores the BIOS that runs when the computer is powered on or otherwise begins execution, a process known as Bootstrapping, or "booting" or "booting up". The BIOS (Basic Input Output System) includes bootfirmware and power management firmware. Newer motherboards use Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) instead of BIOS.
- Buses that connect the CPU to various internal components and to expand cards for graphics and sound.
- The CMOS battery, which powers the memory for date and time in the BIOS chip. This battery is generally a watch battery.
- The video card (also known as the graphics card), which processes computer graphics. More powerful graphics cards are better suited to handle strenuous tasks, such as playing intensive video games.
Expansion cards
An expansion card in computing is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an expansion slot of a computer motherboard or backplane to add functionality to a computer system via the expansion bus. Expansions cards can be used to obtain or expand on features not offered by the motherboard.
Storage devices
A storage device is any computing hardware and digital media that is used for storing, porting and extracting data files and objects. It can hold and store information both temporarily and permanently, and can be internal or external to a computer, server or any similar computing device. Data storage is a core function and fundamental component of computers.
Fixed media
Data is stored by a computer using a variety of media. Hard disk drives are found in virtually all older computers, due to their high capacity and low cost, but solid-state drivesare faster and more power efficient, although currently more expensive than hard drives in terms of dollar per gigabyte,[6] so are often found in personal computers built post-2007.[7] Some systems may use a disk array controller for greater performance or reliability.
Removable media
To transfer data between computers, a USB flash drive or optical disc may be used. Their usefulness depends on being readable by other systems; the majority of machines have an optical disk drive, and virtually all have at least one USB port.
Input and output peripherals
Input and output devices are typically housed externally to the main computer chassis. The following are either standard or very common to many computer systems.
Input
Input devices allow the user to enter information into the system, or control its operation. Most personal computers have amouse and keyboard, but laptop systems typically use a touchpad instead of a mouse. Other input devices include webcams,microphones, joysticks, and image scanners.
Output device
Output devices display information in a human readable form. Such devices could include printers, speakers, monitors or aBraille embosser.
Mainframe computer
A mainframe computer is a much larger computer that typically fills a room and may cost many hundreds or thousands of times as much as a personal computer. They are designed to perform large numbers of calculations for governments and large enterprises.
Departmental computing
In the 1960s and 1970s, more and more departments started to use cheaper and dedicated systems for specific purposes likeprocess control and laboratory automation.
Supercomputer
A supercomputer is superficially similar to a mainframe, but is instead intended for extremely demanding computational tasks. As of June 2016, the fastest supercomputer in the world is the Sunway TaihuLight, inJiangsu, China.[8]
The term supercomputer does not refer to a specific technology. Rather it indicates the fastest computations available at any given time. In mid 2011, the fastest supercomputers boasted speeds exceeding one petaflop, or 1 quadrillion (10^15 or 1,000 trillion) floating point operations per second. Super computers are fast but extremely costly so they are generally used by large organizations to execute computationally demanding tasks involving large data sets. Super computers typically run military and scientific applications. Although they cost millions of dollars, they are also being used for commercial applications where huge amounts of data must be analyzed. For example, large banks employ supercomputers to calculate the risks and returns of various investment strategies, and healthcare organizations use them to analyze giant databases of patient data to determine optimal treatments for various diseases and problems incurring to the country.
Hardware upgrade
When using computer hardware, an upgrademeans adding new hardware to a computer that improves its performance, adds capacity or new features. For example, a user could perform a hardware upgrade to replace thehard drive with a SSD to get a boost in performance or increase the amount of files that may be stored. Also, the user could increase the RAM so the computer may run more smoothly. The user could add a USB 3.0expansion card in order to fully use USB 3.0 devices, or could upgrade the GPU for extra rendering power. Performing such hardware upgrades may be necessary for older computers to meet a programs' system requirements.


Comments
Post a Comment